Santhal Culture & Heritage
- Home
- Santhal Culture & Heritage
Introduction to Santhal community


The Santhal community is one of the largest and most prominent indigenous Adivasi communities of eastern India, with a rich heritage rooted in harmony with nature, collective living, and strong moral values. Their society is guided by customs, oral traditions, music, dance, and a deep respect for land and forests. Social equality, community decision-making, and mutual support form the foundation of Santhal life.
Kanhum Murmu emerged from this cultural and social environment, shaped by the Santhal worldview of justice, courage, and resistance against exploitation. The community’s long history of defending its land, identity, and way of life provided the ideological strength behind his leadership. Understanding the Santhal community is essential to appreciating Kanhum Murmu’s role, as his struggle was not only personal but a collective expression of Santhal identity, dignity, and resilience.

Traditional Practices


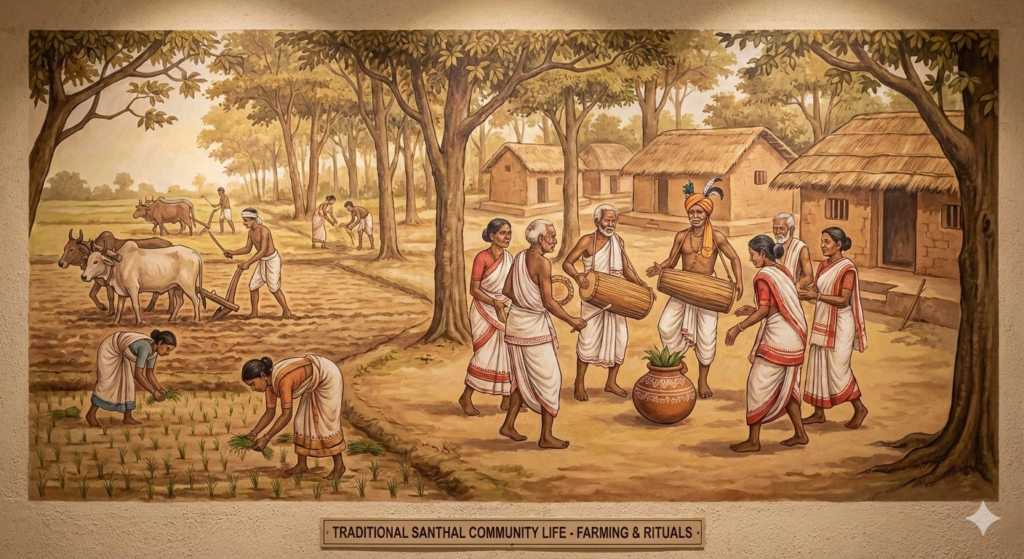
Traditional practices of the Santhal community are deeply connected to nature, seasonal cycles, and collective living. Agriculture, forest stewardship, and sustainable use of natural resources form the basis of daily life. Rituals and ceremonies mark important life events such as birth, marriage, harvest, and remembrance of ancestors.
Community gatherings, village councils, and shared labor reinforce unity, equality, and mutual responsibility. Oral traditions guide moral conduct and social harmony, while festivals strengthen cultural identity. These traditional practices shaped the worldview and leadership values of figures like Kanhum Murmu and continue to preserve Santhal heritage across generations.


Importance of tribal heritage in modern India


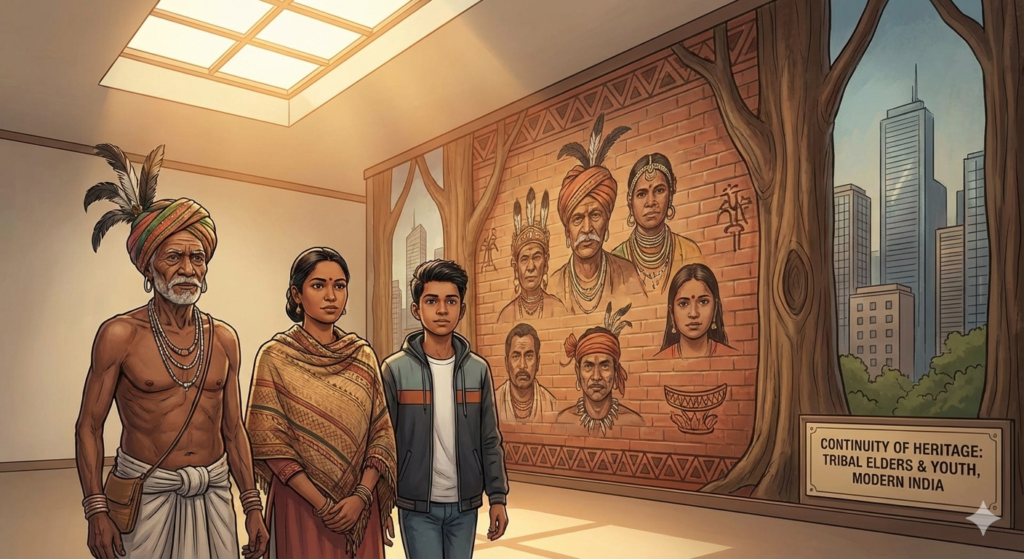
Tribal heritage plays a vital role in shaping modern India’s cultural diversity, environmental knowledge, and social values. Indigenous communities have preserved sustainable ways of living, deep respect for nature, and rich traditions of art, language, and governance that continue to inspire contemporary society.
In today’s rapidly changing world, tribal heritage helps strengthen national identity by honoring inclusivity, resilience, and historical continuity. Recognizing and preserving this heritage ensures that the contributions of tribal communities—such as the Santhal community of Kanhum Murmu—remain an integral part of India’s cultural, social, and educational landscape.